Structure are used to collect related variables in one place .So we collect some different type variables under a same name to better handle.For Example student information can be gathered in one place.This will simplify any further operation over the collected data,because all information items are treated as a single entity called structure.
Following format is used to define a employee structure
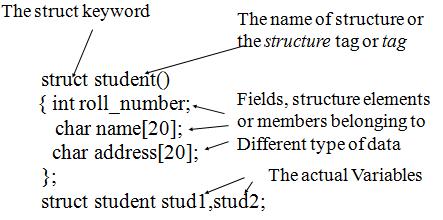
Each Structure can have any data type . It can be int,float,short...etc.Programmer is free to define structure as many as the program required.Each structure have a unique name ,Structure name can be used to define arrays ,variables or passed to function.
Example 1 : Define and Use Structure.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> struct student { char name[20]; int age; int year; float gpa; }; int main() { struct student student_1 ; strcpy(student_1.name,"Max John"); student_1.age=21; student_1.year=2010; student_1.gpa=3.5; printf("Student Name : %s\n",student_1.name); printf("Student Age : %d\n",student_1.age); printf("Student Year : %d\n",student_1.year); printf("Student GPA : %f\n",student_1.gpa); return 0; }
Example 3 : Copying Structure Variables Content to another Variables.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> struct student { char name[20]; int age; int year; float gpa; }; int main() { struct student student_1 , student_2 , student_3 ; strcpy(student_1.name,"Max John"); student_1.age=21; student_1.year=2010; student_1.gpa=3.5; printf("Student(1) Name : %s\n",student_1.name); printf("Student(1) Age : %d\n",student_1.age); printf("Student(1) Year : %d\n",student_1.year); printf("Student(1) GPA : %f\n\n",student_1.gpa); strcpy(student_2.name,student_1.name); student_2.age=student_1.age; student_2.year=student_1.year; student_2.gpa=student_1.gpa; printf("Student(2) Name : %s\n",student_2.name); printf("Student(2) Age : %d\n",student_2.age); printf("Student(2) Year : %d\n",student_2.year); printf("Student(2) GPA : %f\n\n",student_2.gpa); student_3=student_1; printf("Student(3) Name : %s\n",student_3.name); printf("Student(3) Age : %d\n",student_3.age); printf("Student(3) Year : %d\n",student_3.year); printf("Student(3) GPA : %f\n\n",student_3.gpa); return 0; }
In The Next Example We will Enter The Student Data And Make Data Sort According to Student Year .
Example 3 : Entering Data to Structure and Sorting :
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <conio.h> #include <string.h> struct student { char name[20]; int age; int year; float gpa; }; int main() { int i=0 , j=0 , counter=0 ; struct student students[100],swap; char firstname[20]; char secondname[20]; do { printf("Please Enter Student First Name : \n"); scanf("%s",firstname); printf("Please Enter Student Second Name : \n"); scanf("%s",secondname); strcpy(students[i].name,firstname); strcat(students[i].name," "); strcat(students[i].name,secondname); printf("Please Enter Student Age : \n"); scanf("%d",&students[i].age); printf("Please Enter Student Year : \n"); scanf("%d",&students[i].year); printf("Please Enter Student GPA : \n"); scanf("%f",&students[i].gpa); i++; counter++; printf("Do You Want To Add AnyThing Else ? (y/n)\n"); }while (getch()=='y'); for (i=0;i<counter-1;i++){ for (j=i+1;j<counter;j++) { if (students[i].year<students[j].year){ swap=students[j]; students[j]=students[i]; students[i]=swap; } } } for (i=0;i<=counter-1;i++){ printf("Student Name : %s\n",students[i].name); printf("Student Year : %d\n",students[i].year); printf("Student Age : %d\n",students[i].age); printf("Student GPA : %f\n\n",students[i].gpa); } return 0; }
Example 4 : Initializing Structure Variable .
void main { struct student student1 ={"Max John" , 23 , 2010 , 3.45}; pirntf("Student Name : %s\n Student Age : %d\n Student Year : %d\n student GPA :%f\n",student1.name, student1.age,student1.year,student1.gpa); }
We can use two Structure related to each other like in the following example.
Example 5 : Nested Structure Definition.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <conio.h> #include <string.h> struct date { int day; int month; int year; }; struct student { char name[20]; int age; struct date graduate; float gpa; }; int main() { int i=0 , counter=0 ; struct student students[100]; char firstname[20]; char secondname[20]; do { printf("Please Enter Student First Name : \n"); scanf("%s",firstname); printf("Please Enter Student Second Name : \n"); scanf("%s",secondname); strcpy(students[i].name,firstname); strcat(students[i].name," "); strcat(students[i].name,secondname); printf("Please Enter Student Age : \n"); scanf("%d",&students[i].age); printf("Please Enter Student Graduation Data (day-month-year): \n"); scanf("%d%d%d",&students[i].graduate.day,&students[i].graduate.month, &students[i].graduate.year); printf("Please Enter Student GPA : \n"); scanf("%f",&students[i].gpa); i++; counter++; printf("Do You Want To Add AnyThing Else ? (y/n)\n"); }while (getch()=='y'); for (i=0;i<=counter-1;i++){ printf("Student Name : %s\n",students[i].name); printf("Student Graduation Data : %d/%d/%d\n",students[i].graduate.day, students[i].graduate.month,students[i].graduate.year); printf("Student Age : %d\n",students[i].age); printf("Student GPA : %f\n\n",students[i].gpa); } return 0; }
Output :
Example 6: Using Structure With Function .
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <conio.h> #include <string.h> struct date { int day; int month; int year; }; struct student { char name[20]; int age; struct date graduate; float gpa; }; void printall (struct student x){ printf("Student Name : %s\n",x.name); printf("Student Graduation Data : %d/%d/%d\n",x.graduate.day, x.graduate.month,x.graduate.year); printf("Student Age : %d\n",x.age); printf("Student GPA : %f\n\n",x.gpa); } int main() { struct student student1 = {"Max John",23,{23,11,2010},3.5}; printall(student1); return 0; }
Example 7 : Adding Two Complex Number
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct complex { double real ; double imag; }; int main() { struct complex num1 , num2 , result ; printf("Please Enter First complex Number : (Ex: 3 -5 ) \n"); scanf("%lf%lf",&num1.real,&num1.imag); printf("Please Enter Second complex Number :\n"); scanf("%lf%lf",&num2.real,&num2.imag); result.real=num1.real+num2.real; result.imag=num1.imag+num2.imag; printf("Result=(%lf)+(%lf) \n",result.real,result.imag); return 0; }
Example 8 : Adding Two Complex Numbers With Functions
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct complex { double real ; double imag; }; struct complex readnumber () { struct complex a ; printf("please Enter Complex Number : (Ex: 3 -5 )\n"); scanf("%lf%lf",&a.real,&a.imag); return a; } struct complex add (struct complex x , struct complex y){ struct complex z ; z.real=x.real+y.real; z.imag=x.imag+x.imag; return z ; } void printresult (struct complex b){ printf("Result = (%lf) + (%lf)\n",b.real,b.imag); } int main() { struct complex num1 , num2 , result ; num1=readnumber(); num2=readnumber(); result=add(num1,num2); printresult(result); return 0; }







0 Comment to "Structure "
Post a Comment